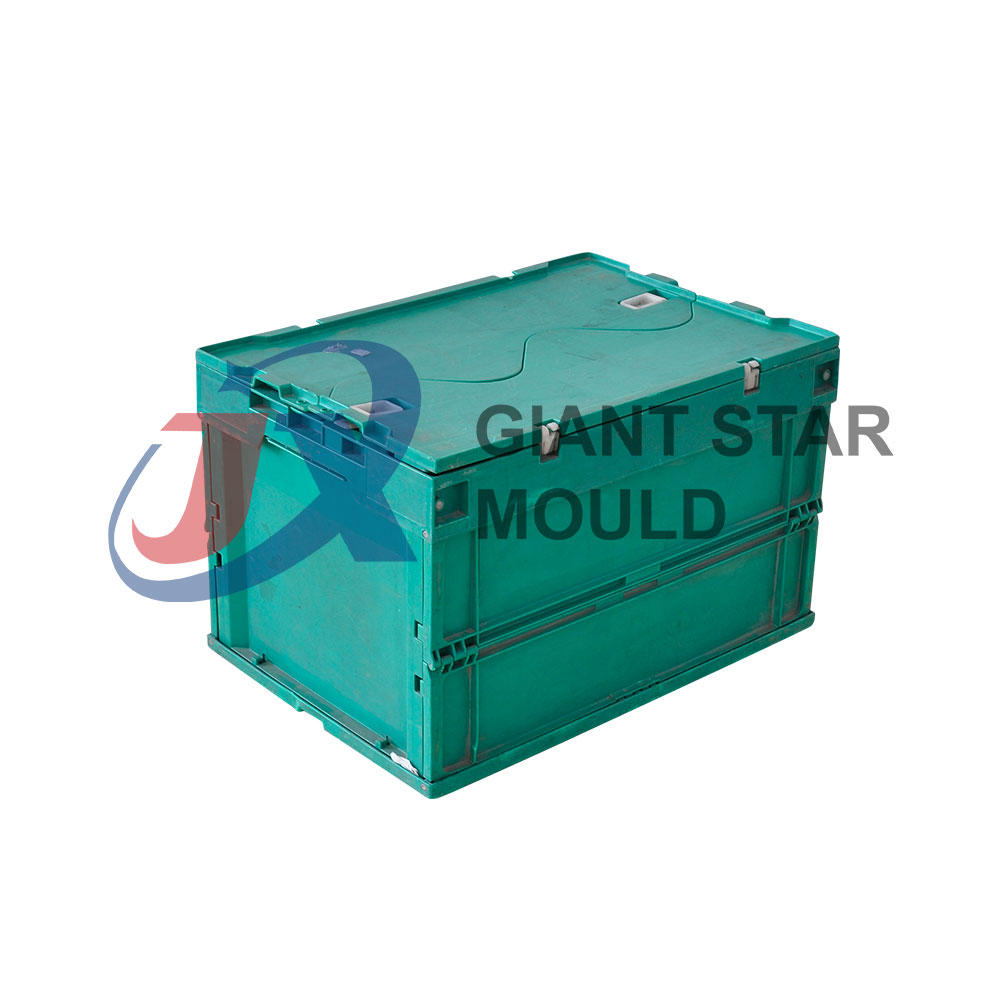
Crate Mould 06
Crate Mould 06
Making a crate mold involves a series of complex steps that require precision, careful planning, and expertise in mold making and manufacturing processes. Here’s a general overview of how crate molds are typically made:
1. Design Preparation
- CAD Model: Start with a detailed 3D CAD model of the crate design, including all features such as handles, stacking features, and any required markings.
- Mold Design: Design the mold based on the CAD model, ensuring proper draft angles, gate locations, and venting provisions.
2. Material Selection
- Choose an appropriate mold material based on factors like the type of plastic to be molded, production volume, and expected mold life. Common materials include steel and aluminum.
3. Machining the Mold
- Rough Machining: Begin by rough machining the mold blocks (core and cavity) to remove excess material and create a basic shape.
- Finish Machining: Use CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines to precisely mill and shape the mold according to the CAD model. This step includes creating the exact contours, features, and surface finishes required for the crate.
4. Heat Treatment (Optional)
- Depending on the material chosen, the mold may undergo heat treatment processes to improve its hardness, toughness, and durability.
5. Assembly
- Assemble the mold components including the core, cavity, ejector pins, cooling channels, and any additional features like slides or lifters.
6. Surface Finishing
- Polish and finish the mold surfaces to the required texture and smoothness. This step ensures that the molded crates have the desired surface appearance.
7. Testing and Adjustments
- Conduct initial testing of the mold with trial runs to check for proper functionality, material flow, cooling effectiveness, and part quality.
- Make adjustments as necessary to optimize the mold for consistent and high-quality crate production.
8. Final Inspection and Approval
- Inspect the completed mold thoroughly to ensure all dimensions, features, and functionalities meet the design specifications and quality standards.
9. Production
- Once the mold is approved, it can be used in production processes to manufacture crates according to the desired specifications.
Additional Considerations:
- Maintenance: Implement a maintenance schedule to keep the mold in optimal condition for prolonged use.
- Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of the mold design, manufacturing process, and any adjustments made for future reference.
Expertise and Collaboration:
- Making a crate mold requires collaboration between designers, mold makers, engineers, and possibly material suppliers to ensure the mold meets all functional and production requirements. Each step involves specialized knowledge and skills to achieve the desired mold quality and performance.