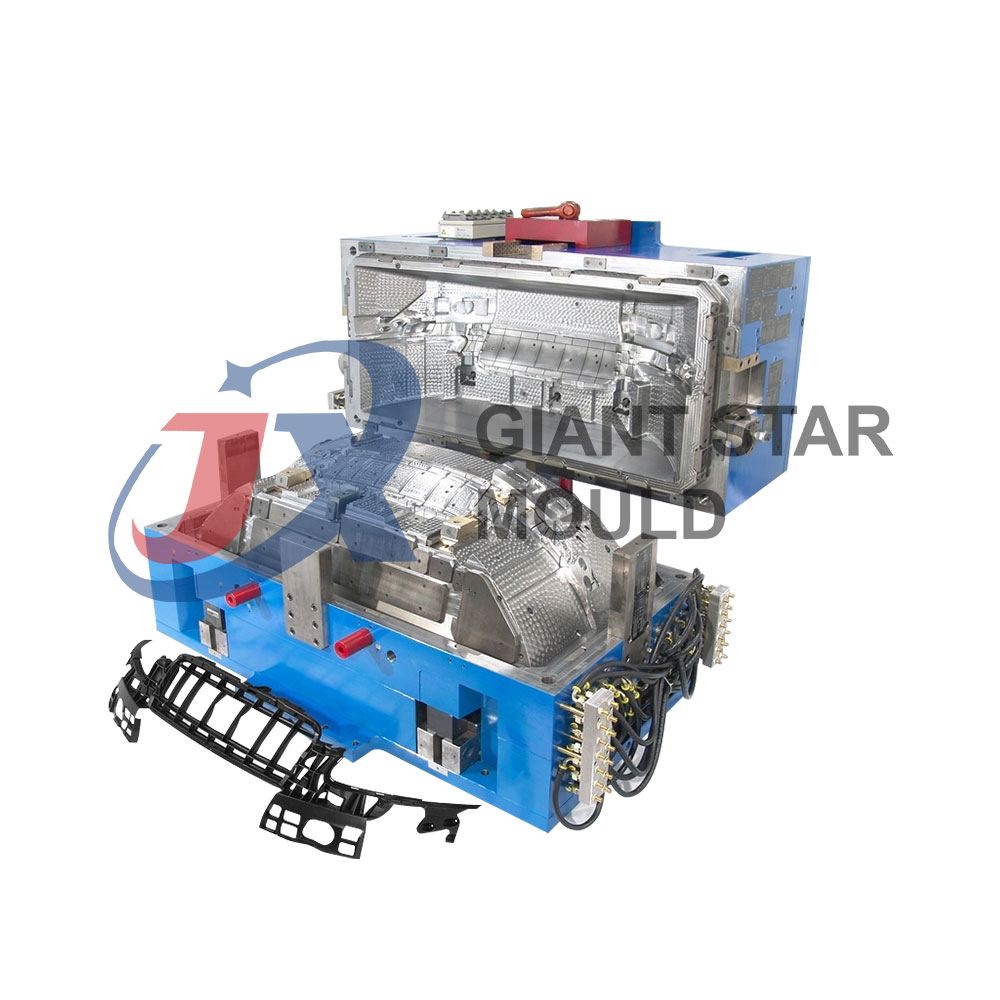
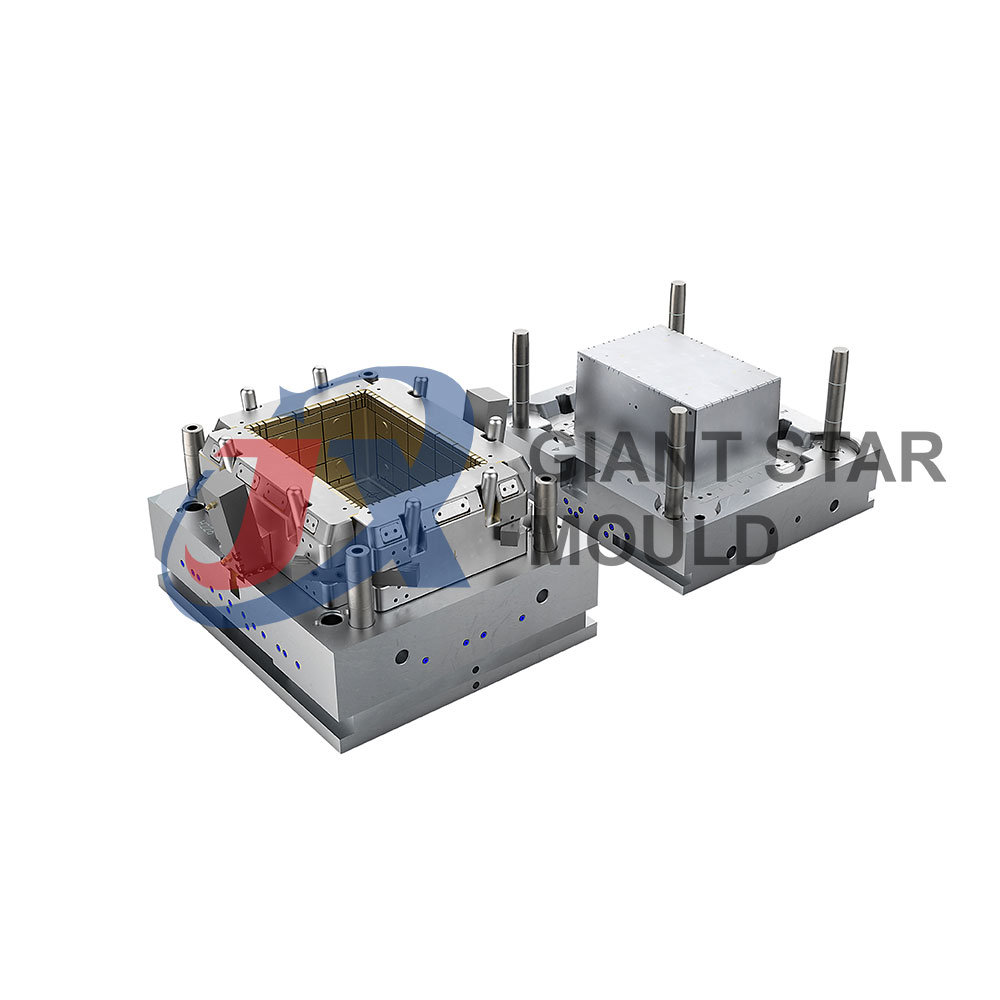
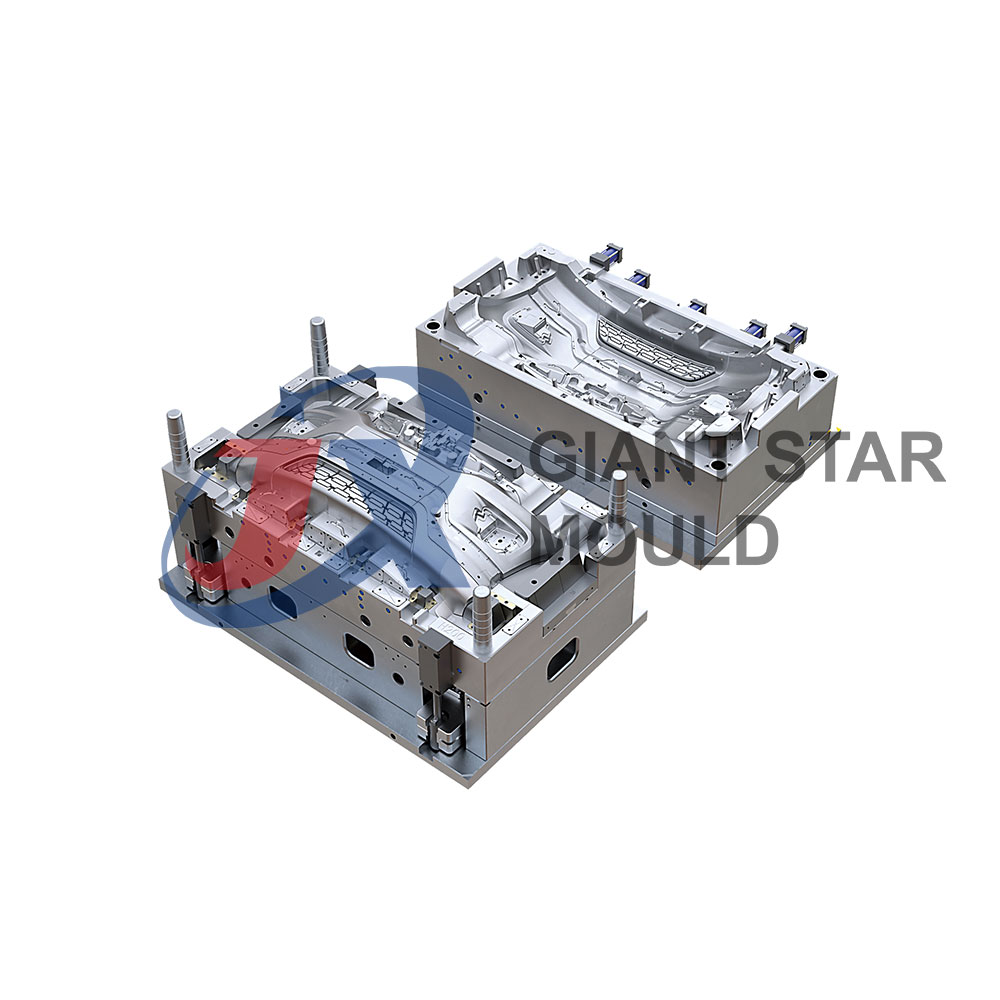
Automotive Plastic Moulds Making
Automotive plastic molds are crucial components in the manufacturing process of various plastic parts used in vehicles. These molds are used to shape molten plastic into specific forms, such as dashboards, bumpers, interior panels, and exterior body parts. They play a significant role in the production of lightweight, durable, and cost-effective automotive components.
Here are some key points about automotive plastic molds:
Design and Engineering: Automotive plastic molds are meticulously designed and engineered to meet the precise specifications of the final product. This involves CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing) technology to create highly detailed and accurate molds.
Material Selection: The choice of mold material is critical, as it affects the durability, precision, and lifespan of the mold. Common materials used for automotive plastic molds include steel, aluminum, and various alloys. The selection depends on factors such as production volume, part complexity, and budget considerations.
Injection Molding Process: Injection molding is the most commonly used method for manufacturing automotive plastic parts. The process involves injecting molten plastic material into the cavity of the mold under high pressure. Once the plastic cools and solidifies, the mold is opened, and the finished part is ejected.
Complexity and Precision: Automotive plastic molds can be highly complex, especially for intricate parts with precise geometries and tight tolerances. Advanced molding techniques, such as multi-cavity molds and hot runner systems, are often used to increase efficiency and reduce production costs.
Surface Finish and Texture: The surface finish of automotive plastic parts is crucial for aesthetic appeal and functional performance. Molds can be designed to impart specific textures and finishes onto the final parts, such as matte, glossy, or textured surfaces.
Tooling Maintenance: Proper maintenance of automotive plastic molds is essential to ensure consistent quality and prolong the lifespan of the tooling. Regular cleaning, inspection, and repair of molds help prevent defects and production downtime.
Customization and Prototyping: Automotive manufacturers often require custom molds for unique parts or prototypes. Rapid prototyping technologies, such as 3D printing, are increasingly used to quickly produce prototype molds for testing and validation before full-scale production.
Overall, automotive plastic molds are integral to the production of high-quality plastic components used in modern vehicles. They enable manufacturers to achieve cost-effective production, lightweight design, and flexibility in part customization.